Text analysis: Growth and tropism
Do the plants move?
Animals can move around to get what they need to survive. But did you know plants can also move? They can’t get up and run, but they can move closer to food and water, and away from danger.
Tropism is when a plant moves in response to an external stimulus in the environment. Positive tropism is when a plant moves towards a stimulus. Negative tropism is when a plant moves away from a stimulus.
Plants can respond to several different aspects of their environments. These include light, gravity, water and contact with objects.
Let’s focus on phototropism and heliotopism
Phototropism

Phototropism is when plants move in response to light. You can do an experiment to see this at home. Give any house plant a single source of light, such as a window. Soon the plant will begin bending towards the light. It grows in that direction to get more light for photosynthesis.
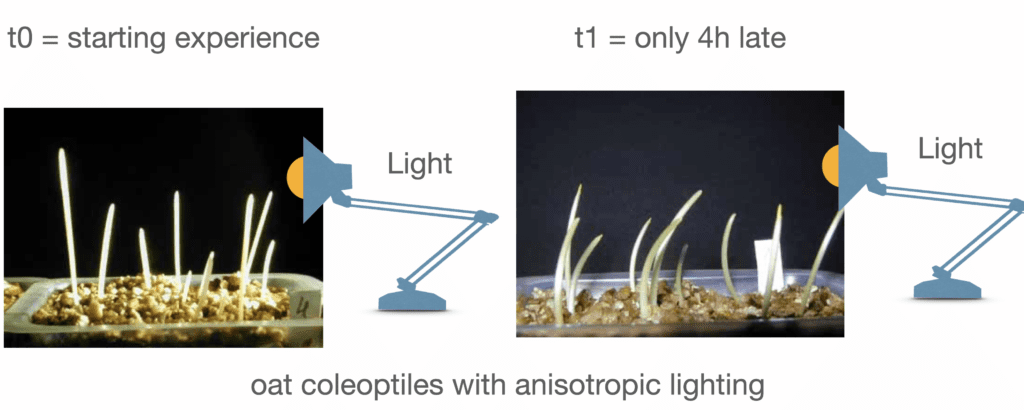
The movements of plants were first described comprehensively by Charles Darwin in 1880 in his seminal work « The power of movement in plants ». The theory that the plant hormone auxin could play a role in plants bending toward a light source was first proposed in 1937 by the Dutch researcher Frits Went in the Cholodny-Went model.
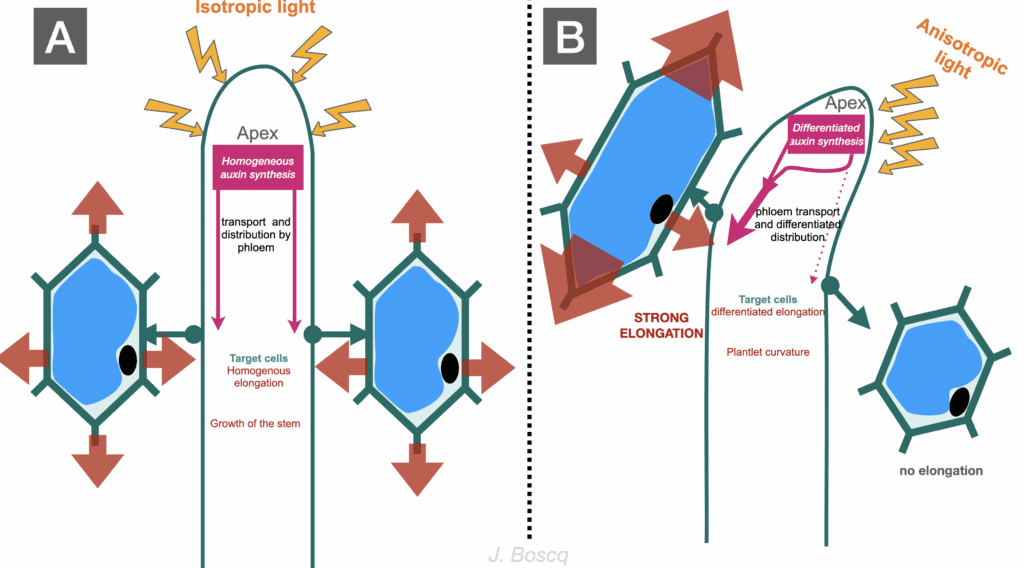
How auxin is involved in tilting the plant towards the light? Auxin, which is a plant hormon, is responsible for elongating the shaded side of a plant’s stem. The growing stem on the opposite side of the light grows faster than the light side of the plant. This is because the hormone accumulates on the shady side, causing the cells on this side to elongate and allowing the stem to move towards the light, so that the leaves are in the best possible position in relation to the light.
Just below a diagram of the mechanism of the cell’s elongation by the auxin
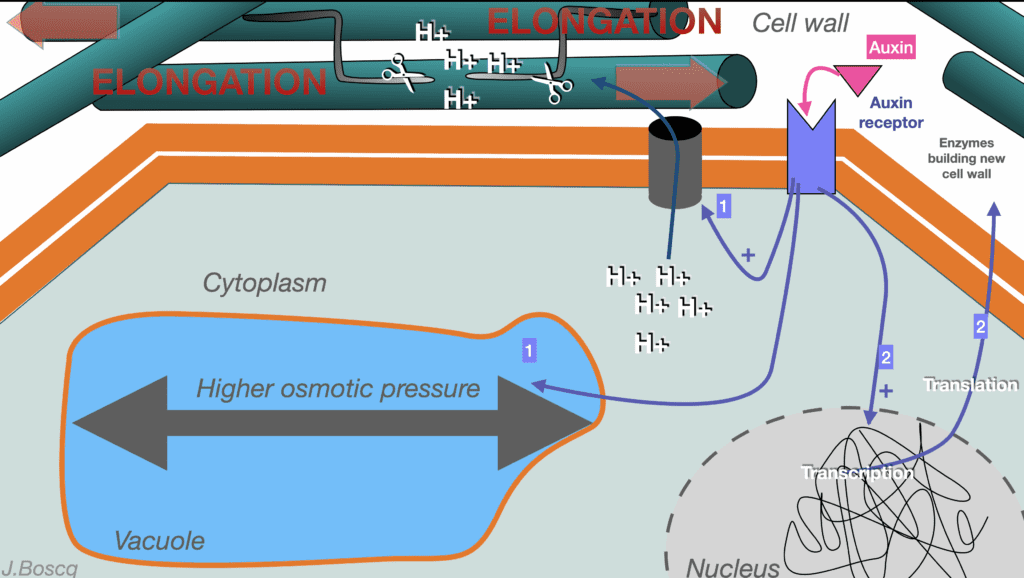
Historic experiences driving to understand the way of auxin regulation
Heliotopism
Heliotropism is a particular phototropism. It is the way that the plant follow the direction of the light all the day from east to west.
Sunflowers perform their daily dance from east to west by the coordinate action of two mechanisms. Light-signaling pathways set a basic rate of growth for the plant, based on available light. The apex of the plant is the most sensitive to light. The circadian or internal clock of the plant is influenced by the direction of light and causes the stem to grow more on one side than the other.
At the final stage of flower development, called anthesis, sunflowers conclude their solar tracking ways and turn their flowerheads eastward. These east-facing sunflowers heat up more quickly in the morning, making them more attractive to pollinating insects, such as honeybees.
Vocabulary:
Tropism: the turning of all or part of an organism in a particular direction in response to an external stimulus. (Tropisme)
Tilting: move or cause to move into a sloping position (basculement)
Circadian: recurring naturally on a twenty-four-hour cycle, even in the absence of light fluctuations. (Circadien)
Apex: the top or highest part of something, especially one forming a point. (Apex)
Sunflower: a tall North American plant of the daisy family, with very large golden-rayed flowers. Sunflowers are cultivated for their edible seeds, which are an important source of oil for cooking and margarine. (Tournesol)
To go further : Let’s talk sciences : All the tropisms
Video : Plants in space !!!

