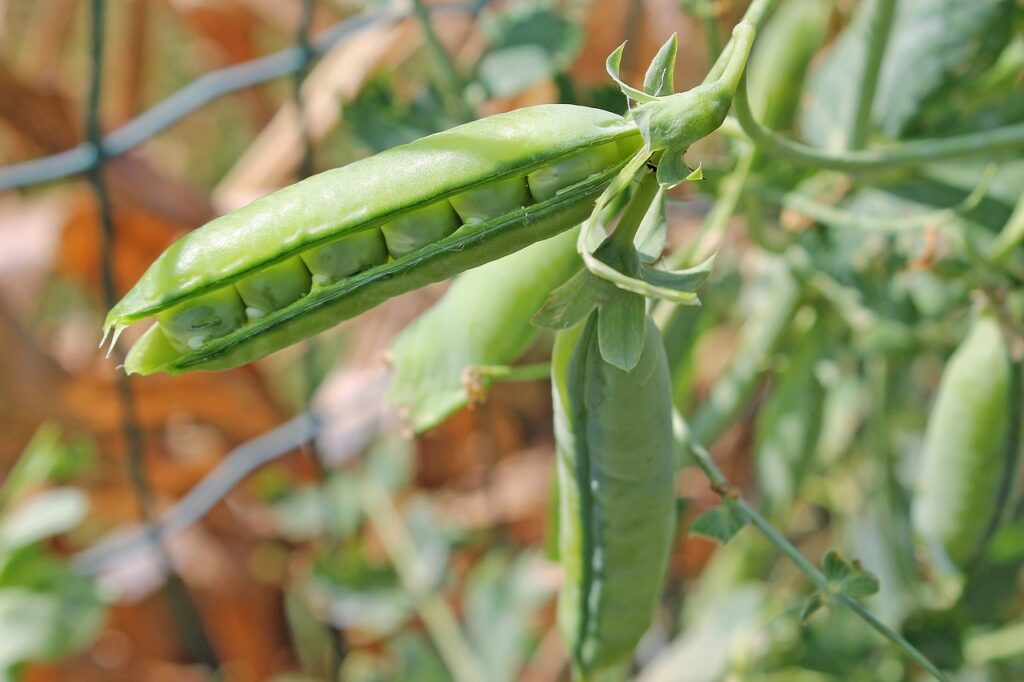
Lab activity: Crosses and analysis of results

Gregor Mendel, often referred to as the “Father of Genetics,” was an Austrian monk who revolutionized our understanding of inheritance. In the mid-19th century, Mendel conducted groundbreaking experiments on pea plants in the garden of his monastery, seeking to uncover how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
At the time, the prevailing belief was that offspring were a “blend” of their parents’ traits, much like mixing colors. However, Mendel’s meticulous observations and experiments revealed a different story. By cross-breeding pea plants with specific, contrasting traits—such as tall vs. short plants or yellow vs. green seeds—he discovered that traits do not blend but are inherited as discrete units. This is the roots of genetics!
1- Understanding the laws of genetics
Use the following video to answer the questions and identify the vocabulary specific to genetics, defining it at the end.
a) What are the phenotypes of the first peas Mendel crosses? Are they purebred?
b) What did he find when the offspring grew?
c) When the second filial generation arrived F2, what did he observe?
d) What can you say about the traits or the alleles of the F1 offspring ?
e) What is a gene ?
f) Why do you have at least 2 alleles for each gene (identical or not)?
g) What does hetero mean?
h) How do you write the genotypes in english, and what do you need to watch out for to avoid being confused?
i) In pea pods, green is dominant over yellow. If these are the genotypes or allele combinations, what are the phenotypes?
j)Assuming tallness is dominant. What would the genotype look like for a man who’s homozygous for tall? And what are the possible gamete combinations?
Vocabulary to define : Traits, to breed, wrinkly or round seeds, purebred trait, offspring, F1 generation, F2 generation, gene, dominant and recessive allele, heterozygous, homozygous, genotype, phenotype
2- It’s your turn to analyse crosses
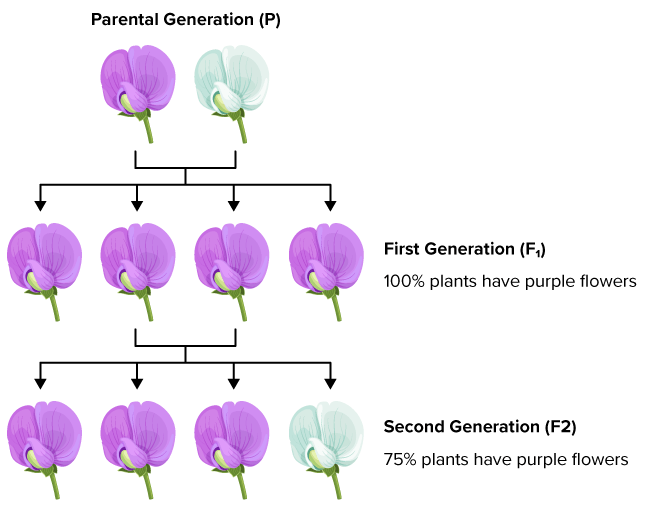
A- Flowers
What conclusions can you draw about this cross?
B- Seeds
In pea plants, round peas (R) are dominant to wrinkled peas (r). You do a test cross between a pea plant with wrinkled peas (genotype rr) and a plant of unknown genotype that has round peas. You end up with three plants, all which have round peas.
1- From this data, can you tell if the round pea parent plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous?
2- If the round pea parent plant is heterozygous, what is the probability that a random sample of 3 progeny peas will all be round?
C- Dihybridism
=> Calculate and predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring of dihybrid crosses involving unlinked autosomal genes.
R = Dominant allele for shape (round)
r = recessive allele for seed shape (wrinkled)
Y = Dominant allele for seed color (Yellow)
y = recessive allele for seed color (green)
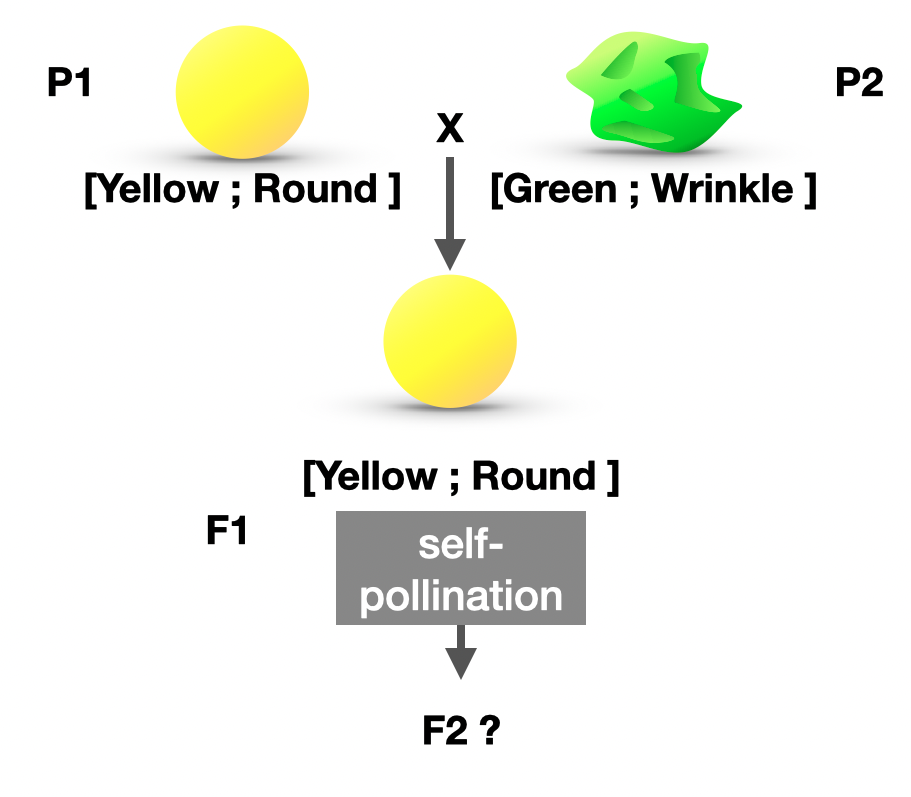
To better understand:
To go further: Fifty shades of peas podcast

